|
Thorsten Becker
The University of Texas at Austin Geodynamics research |

|
[news] [teaching] [team] [publications] [CV] [downloads] [contact]
[geodynamics] [seismology] [fieldwork] [downloads] [lab]
[subduction] [dynamic topography] [global dynamics] [western US] [anisotropy]
Megathrust Modeling Framework (MTMOD)
A five-year, collaborative, NSF FRES funded effort to advance integrative modeling capabilties within the megathrust context to advance the use of physics-based models for earthquake hazard asssessment. Read more on the MTMOD web page.Post- and co-seismic deformation in subduction zones
A number of collaborative projects with colleagues at ERI U Tokyo, Purdue, USC, and UT. We study the deformation and crustal stress before, during, and after the 2011 M9 Tohoku-oki earthquake as constrained from geodetic measurements and finite element forward and adjoint inverse modeling.
- Puel, S., Becker, T.W., Villa, U., Ghattas, O., and Liu, D.: Volcanic arc rigidity variations illuminated by coseismic deformation of the 2011 Tohoku-oki M9, Science Adv., 10, doi:10.1126/sciadv.adl4264, 2024. (PDF)
- Becker, T. W., Hashima, A., Freed, A. M., and Sato, H.: Stress change before and after the 2011 M9 Tohoku-oki earthquake. Earth Planet Sci. Lett., 504, 174-184, 2018. (PDF)
- Freed, A. M., Hashima, A., Becker, T. W., Okaya, D. A., Sato, H., and Hatanaka. Y.: Resolving depth-dependent subduction zone viscosity and afterslip from postseismic displacements following the 2011 Tohoku-oki, Japan earthquake. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 459, 279-290, 2017. (PDF)
- Hashima, A., Becker, T. W., Freed, A. M., Sato, H., and Okaya, D. A.: Coseismic deformation due to the 2011 Tohoku-oki earthquake: influence of 3-D elastic structure around Japan. Earth, Planet., Space, 68, 159, doi:10.1186/s40623-016-0535-9, 2016. (PDF)
- Seminar on related topics at DGS, UT Austin, March 2017.
Long-term subduction dynamics
Upper mantle slab dynamics
We explore how regional and global subduction dynamics as well as the rheology and geology of the lithosphere and mantle can affect slab morphologies, plate velocities including trench motions, seismicity, overriding plate deformation and magmatism. Regional applications include the Caribbean, Mediterranean, Colombia, Middle East, Taiwan, and the western Pacific domain.Slab-slab, slab-plume, and plume-slab interactions
We explore how mantle convection is linked with tectonic deformation based on understanding the interactions between system components, and for key regional natural laboratories.- Conrad, E. M., Faccenna, F., Holt, A. F., and Becker, T. W.: Tectonic reorganization of the Caribbean plate system in the Paleogene driven by Farallon slab anchoring. G-Cubed, 25, doi:10.1029/2024GC011499, 2024. (PDF)
- Heilman, E. and Becker, T. W.: Plume-driven subduction termination in 3-D mantle convection models. G-Cubed, doi:10.1029/2024GC011523, 2024. (PDF)
- Heilman, E. and Becker, T. W.: Plume-slab interactions can shut off subduction. Geophys. Res. Lett., 49, e2022GL099286, 2022. (PDF)
- Holt, A. H., Royden, L. H., Becker, T. W., and Faccenna, F.: Slab interactions in 3-D subduction settings: The Philippine Sea Plate region. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 489, 72-83, 2018. (PDF)
- Faccenna, C., Holt, A. F., Becker, T. W., Lallemand, S., and Royden, L. H.: Dynamics of the Ryukyu/Izu-Bonin-Marianas double subduction system. Tectonophys., 746, 229-238, 2018. (PDF)
- Holt, A. F., Royden, L. H., and Becker, T. W.: The dynamics of double slab subduction. Geophys. J. Int., 209, 250-265, 2017. (PDF, supp. mov.)
- Jagoutz, O., Royden, L., Holt, A. F., and Becker, T. W.: Anomalously fast convergence between India and Eurasia caused by double subduction. Nature Geosc., 8, 475-478, 2015. (PDF, supp.mat.)
- Faccenna, C., Becker, T. W., Jolivet, L., and Keskin, M.: Mantle convection in the Middle East: Reconciling Afar upwelling, Arabia indentation and Aegean trench rollback. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 375, 254-269, 2013.
- Faccenna, C., Becker, T. W., Lallemand, S., Lagabrielle, Y., Funiciello, F., and Piromallo, C.: Subduction-triggered magmatic pulses. A new class of plumes? Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 209, 54-68, 2010. (PDF)
Crust, slab, and mantle rheology controls on tectonics
- Grima, A. G. and Becker, T. W.: The role of continental heterogeneity on the evolution of continental plate margin topography at subduction zones. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 642, 118856, 2024. (PDF)
- Becker, T.W., Behr, W.M., Brizzi, S., and Faccenna, C.: Subduction
dynamics and surface-deep mantle interactions. Keynote presentation
at the CSMDS meeting, Boulder CO, 2023.
- Behr, W. M., Holt, A. F., Becker, T. W., and Faccenna, C.: The effects of plate interface rheology on subduction kinematics and dynamics. Geophys. J. Int., 230, 796-812, 2022. (PDF)
- Gerya, T. V., Bercovici, D., and Becker, T. W.: Dynamic slab segmentation due to brittle-ductile damage in the outer rise. Nature, 599, 245-250, 2021. (PDF)
- Brizzi, S., Becker, T.W., Faccenna, C., Behr, W.M., van Zelst, I., Dal Zilio, L. and van Dinther, Y.: The role of sediment accretion and buoyancy on subduction dynamics and geometry. Geophys. Res. Lett., 48, doi:10.1029/2021GL096266, 2021. (PDF)
- Fuchs, L. and Becker, T. W.: Role of strain-dependent weakening memory on the style of mantle convection and plate boundary stability. Geophys. J. Int., 218, 601-618, 2019. (PDF)
- Behr, W. M. and Becker, T. W.: Sediment control on subduction plate speeds. Earth Planet Sci. Lett., 502, 166-173, 2018. (PDF, JSG press release)
- Freed, A. M., Hashima, A., Becker, T. W., Okaya, D. A., Sato, H., and Hatanaka. Y.: Resolving depth-dependent subduction zone viscosity and afterslip from postseismic displacements following the 2011 Tohoku-oki, Japan earthquake. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 459, 279–290, 2017. (PDF)
- Holt, A. F. and Becker, T. W.: The effect of a power-law mantle viscosity on trench retreat rate. Geophys. J. Int., 208, 491-507, 2017. (PDF)
- Holt, A. F., Buffett, B. A., and Becker, T. W.: Overriding plate thickness control on subducting plate curvature. Geophys. Res. Lett., 42 , doi:10.1002/2015GL063834, 3802-3810, 2015. (PDF)
- Bailey, I. W., Alpert, L. A., Becker, T. W., and Miller, M. S.: Co-seismic deformation of deep slabs based on summed CMT data. J. Geophys. Res., 117, B04404, doi:10.1029/2011JB008943, 2012. (PDF)
- Buffett, B. and Becker, T. W.: Bending stress and dissipation in subducted lithosphere. J. Geophys. Res., 117, B05413, doi:10.1029/2012JB009205, 2012. (PDF)
- Miller, M. S. and Becker, T. W.: Mantle flow deflected by interactions between subducted slabs and cratonic keels. Nature Geosc., 5, 726-730, 2012. (PDF)
- Gérault, M. and Becker, T. W. and Kaus, B. J. K. and Faccenna, L. and Moresi, L. N. and Husson, L.: The role of slabs and oceanic plate geometry for the net rotation of the lithosphere, trench motions, and slab return flow. Geochem., Geophys., Geosys., 13, Q04001, doi:10.1029/2011GC003934, 2012. (PDF)
- Alpert, L. A., Becker, T. W., and Bailey, I. W.: Global slab deformation and centroid moment tensor constraints on viscosity. Geochem., Geophys. Geosys., 11,(Q12006), doi:10.1029/2010GC003301, 2010. (PDF)
- Funiciello, F., Faccenna, C., Heuret, A., Di Giuseppe, E., Lallemand, S., and Becker, T. W.: Trench migration, net rotation and slab-mantle coupling. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 271, 233-240, 2008. (PDF)
- Enns, A., Becker, T. W., and Schmeling, H.: The dynamics of subduction and trench migration for viscosity stratification. Geophys. J. Int., 160, 761-775, 2005. (PDF)
Subduction and orogeny
- Grima, A. G. and Becker, T. W.: The Role of continental heterogeneity on the evolution of continental plate margin topography at subduction zones. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett.. 642, 118856, 2024. (PDF)
- Miller, M. S., Zhang, P., Dahlquist, M. P., West, A. J., Becker, T. W., and Harris, C. W.: Inherited lithospheric structures control arc-continent collisional heterogeneity. Geology, 49, 2021. (PDF)
- Behr, W. M. and Becker, T. W.: Sediment control on subduction plate speeds. Earth Planet Sci. Lett., 2018. (PDF, JSG press release)
- Wagner, L., Jaramillo, J. S., Ramírez-Hoyos, L. F., Monsalve, G., Cardona, A. and Becker, T. W.: Transient slab flattening beneath Colombia. Geophys. Res. Lett., 44, 6616-6623, doi:10.1002/2017GL073981, 2017. (PDF)
- Faccenna, C., Oncken, O., Holt, A. F., and Becker, T. W.: Initiation of the Andean orogeny by lower mantle subduction. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 463, 189-201, 2017. (PDF)
- Sternai, P., Avouac, J.-P., Jolivet, L., Faccenna, C., Gerya, T., Becker, T. W., and Menant, A.: Sub-crustal forcing on the tectonics and topography along the eastern Tibetan margin. J. Geodyn., 184-197, 2016. (PDF)
- Becker, T. W., Schaeffer, A. J., Lebedev, S., and Conrad, C. P.: Toward a generalized plate motion reference frame. Geophys. Res. Lett., 40, doi:10.1002/2015GL063695, 2015. (PDF, supp. mat.)
- Holt, A. F., Becker, T. W., and Buffett, B. A.: Trench migration and overriding plate stress in dynamic subduction models. Geophys. J. Int., 201, 172-192, 2015. (PDF)
- Faccenna, C., Becker, T. W., Auer, L., Billi, A., Boschi, L., Brun, J.-P., Capitanio, F. A., Funiciello, F., Horvath, F., Jolivet, L., Piromallo, C., Royden, L., Rossetti, F., and Serpelloni, E.: Mantle dynamics in the Mediterranean. Rev. Geophys., 52, doi:10.1002/2013RG000444, 2014. (PDF)
- Boschi, L., Faccenna, C., and Becker, T. W.: Mantle structure and dynamic topography in the Mediterranean Basin. Geophys. Res. Lett., 37 (L20303), doi:10.1029/2010GL045001, 2010. (PDF)
- Faccenna, C. and Becker, T. W.: Shaping mobile belts by small-scale convection. Nature, 465, 602-605, 2010. (PDF, News and views)
Slab pull, plate and trench motions, and lithospheric deformation
- Hua, J., Grand, S. P., Becker, T. W., Janiszewski, H., Liu, C., Trugman, D., and Zhu, H: Seismic full-waveform tomography of active cratonic thinning beneath North America consistent with slab-induced dripping. Nature Geosc., doi:10.1038/s41561-025-01671-x, 2025. (PDF)
- Clennett, E. J., Holt, A. F, Tetley, M. G., Becker, T. W., and Faccenna, C.: Assessing plate reconstruction model using plate driving force consistency tests. Sci. Rep., 19, 10191, 2023. (PDF)
- Alpert, L. A., Miller, M. S., Becker, T. W., and Allam, A. A.: Structure beneath the Alboran from geodynamic flow models and seismic anisotropy. J. Geophys. Res., 118, 4265-4277, doi:10.1002/jgrb.50309, 2013. (PDF)
- Faccenna, C., Becker, T. W., Lallemand, S., and Steinberger, B.: On the role of slab pull in the Cenozoic motion of the Pacific. Geophys. Res. Lett., 39, L03305, doi:10.1029/2011GL050155, 2012. (PDF)
- Becker, T. W. and Faccenna, C.: A review of the role of subduction dynamics for regional and global plate motions. In: Subduction Zone Geodynamics, Lallemand, S. and Funiciello, F. (eds), Int. J. Earth Sci., 3-34, 2009. (PDF)
- Kaus, B, Liu, Y., Becker, T. W., Yuen, D., and Shi, Y.: Lithospheric stress-states predicted from long-term tectonic models: influence of rheology and possible application to Taiwan. J. Asian Earth Sci., 36, 119-134, 2009. (PDF)
- Kaus, B. J. P., Steedman, C., and Becker, T. W.: From passive continental margin to mountain belt: insights from analytical and numerical models and application to Taiwan. Phys. Earth Planet. Int., 171, 235-251, 2008. (PDF)
- Kaus B. J. P., Becker T. W.. A numerical study on the effects of surface boundary conditions and rheology on slab dynamics. Bolletino di Geofisica, 49(2), 177-182, 2008. (PDF)
- Faccenna, C., Heuret, A., Funiciello, F., Lallemand, S., and Becker, T. W.: Predicting trench and plate motion from the dynamics of a strong slab. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 257, 29-36, 2007. (PDF)
- Piromallo, C., Becker, T. W., Funiciello, F., and Faccenna, C.: Three-dimensional instantaneous mantle flow induced by subduction, Geophys. Res. Lett., 33, L08304, doi:10.1029/2005GL025390, 2006. (PDF)
- Faccenna, C., Becker, T. W., Lucente, F. P., Jolivet, L. and Rossetti, F.: History of Subduction and Back-arc Extension in the Central Mediterranean. Geophys. J. Int., 145, 809, 2001. (PDF)
- Becker, T. W., Faccenna, C., O'Connell, R. J., and Giardini, D.: The development of slabs in the upper mantle: insights from experimental and laboratory experiments. J. Geophys. Res., 104, 15,207-15,226, 1999. (PDF)
Subduction as imaged by structural seismology
We investigate how the global subduction system is reflected in mantle heterogeneity, and what this implies for time-dependent plate tectonics, orogeny, mass transport, depth, and thermo-chemical convection.
- Hua, J., Grand, S. P., Becker, T. W., Janiszewski, H., Liu, C., Trugman, D., and Zhu, H: Seismic full-waveform tomography of active cratonic thinning beneath North America consistent with slab-induced dripping. Nature Geosc., doi:10.1038/s41561-025-01671-x, 2025. (PDF)
- Porritt, R., Becker, T.W., Boschi, L., and Auer, L.: Multi-scale, radially anisotropic shear wave imaging of the mantle underneath the contiguous United States through joint inversion of USArray and global datasets. Geophys. J. Int., 2021. (PDF, SI, SAVANI-US model download)
- Faccenna, F., Becker, T. W., Holt, A. F., and Brun, J. P.: Mountain building, mantle convection, and supercontinents: Holmes (1931) revisited. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 564, Frontiers, 116905, 2021. (PDF)
- Faccenna, C., Oncken, O., Holt, A. F., and Becker, T. W.: Initiation of the Andean orogeny by lower mantle subduction. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 463, 189-201, 2017. (PDF)
- Schmandt, B., Jacobsen, S. D., Becker, T. W., Liu, Z., and Dueker, K. G.: Dehydration melting at the top of the lower mantle. Science, 334, 1265-1268, 2014. (PDF)
- Faccenna, C., Becker, T. W., Conrad, C. P., and Husson, L.: Mountain building and mantle dynamics. Tectonics, 32, 1-15, doi:10.1029/2012TC003176, 2013. (PDF)
- Steinberger, B., Torsvik, T. H., and Becker, T. W.: Subduction to the lower mantle - a comparison between geodynamic and tomographic models. Solid Earth, 3, 415-432, 2012. (PDF)
- Boschi, L. and Becker, T. W.: Vertical coherence in mantle heterogeneity from global seismic data. Geophys. Res. Lett., 38, (L20306), doi:10.1029/2011GL049281, 2011. (PDF)
- Becker, T. W. and Boschi, L.: A comparison of tomographic and geodynamic mantle models, Geochem., Geophys., Geosys., 3, 2001GC000168, 2002. (PDF)
NSF-CD project Program to Investigate Convective Alboran Sea System Overturn (PICASSO)
We were part of a multi-institutional, multi-disciplinary continental dynamics research effort funded by NSF-CD to study subduction dynamics and lithospheric delamination mechanisms in the westernmost terminus of the Tethyan collision.- Conference presentation summarizing some of the USC led findings:
- Miller, M. S.: Pockets, conduits, channels, and plumes: links to volcanism and orogeny in the western Meditteranean. Presentation at CIDER 2016, (video)
- Geodynamics team project publications
- Sun, D., Miller, M. S., Holt, A. F., and Becker, T. W.: Hot upwelling conduit beneath the Atlas Mountains, Morocco. Geophys. Res. Lett., 41, 8037-8044, doi:10.1002/2014GL061884, 2014. (PDF, supp. mat.)
- Faccenna, C., Becker, T. W., Auer, L., Billi, A., Boschi, L., Brun, J.-P., Capitanio, F. A., Funiciello, F., Horvath, F., Jolivet, L., Piromallo, C., Royden, L., Rossetti, F., and Serpelloni, E.: Mantle dynamics in the Mediterranean. Rev. Geophys., 52, doi:10.1002/2013RG000444, 2014. (PDF)
- Miller, M. S. and Becker, T. W.: Reactivated lithospheric-scale
discontinuities localize dynamic uplift of the Moroccan Atlas
Mountains. Geology, doi:10.1130/G34959,
2014. (PDF)
- Miller, M. S. and Becker, T. W.: Reactivated lithospheric-scale discontinuities localize dynamic uplift of the Moroccan Atlas Mountains: Comment - Reply. Geology, 42, 338, 2014. (PDF)
- Nature Geoscience highlight by Whitchuch
- Alpert, L. A., Miller, M. S., Becker, T. W., and Allam, A. A.: Structure beneath the Alboran from geodynamic flow models and seismic anisotropy. J. Geophys. Res., 118, 4265--4277, doi:10.1002/jgrb.50309, 2013. (PDF)
- Faccenna, C., Becker, T. W., Jolivet, L., and Keskin, M.: Mantle convection in the Middle East: Reconciling Afar upwelling, Arabia indentation and Aegean trench rollback. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 375, 254-269, 2013. (PDF)
- Miller, M. S., Allam, A. A., Becker, T. W., Di Leo, J., and Wookey, J.: Constraints on the geodynamic evolution of the westernmost Mediterranean and northwestern Africa from shear wave splitting analysis. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 375, 234-243, 2013. (PDF)
- Becker, T. W. and Faccenna, C.: Mantle conveyor beneath the Tethyan collisional belt. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 310, 453-461, 2011. (PDF)
- Faccenna, C. and Becker, T. W.: Shaping mobile belts by small-scale convection. Nature, 465, 602-605, 2010. (PDF)
- Conference presentation summarizing some of the USC led findings:
Effect of elasticity on mantle convection
We investigate the role of visco-elasticity for the formation of Rayleigh-Taylor type instabilities and lithospheric detachments.
- Kaus, B. J. P. and Becker, T. W.: Effects of elasticity on the Rayleigh-Taylor instability: implications for large-scale geodynamics. Geophys. J. Int., 168, 843-862, 2007. (PDF)
Short course: Subduction zone modeling
Short course held the University of Roma TRE, April 2011, on numerical and analog modeling of subduction zones and slab dynamics on regional on global scales. Part of the Geodynamics Graduate School at Roma TRE.Lecture slides (as of 2011):
Modeling Collaboratory for Subduction RCN
A four year, collaborative, NSF funded Research Collaboration Network to plan for Modeling Collaboratory for Subduction to address the physics of megathrust and volcano subduction systems with an eye toward decadal scale forecasting in multi-sensor monitoring networks. Read more on the MCS RCN web page.Dynamic origin of surface topography
A multi-project effort to contribute to our understanding of the origin of surface topography and uplift, and the general mechanisms of mountain building and continental dynamics. We try to disentangle the effects of hydrology, tectonics, erosion, and mantle flow (AKA dynamic topography) for building and destroying topography and causing intraplate deformation.
Cordillera
Regional studies focusing on the Cordilleran oregenies of North and South America.
- Becker, T.W., Behr, W.M., Brizzi, S., and Faccenna, C.: Subduction
dynamics and surface-deep mantle interactions. Keynote presentation
at the CSMDS meeting, Boulder CO, 2023.
- Lau, N., Borsa, A. A. and Becker, T. W.: Present-day crustal vertical velocity field for the Contiguous United States. J. Geophys. Res., 125, doi:10.1029/2020JB020066, 2020. (PDF)
- Siravo, G., Faccenna, C., Gerault, M., Becker, T. W., Fellin, M. G., Herman, F. and Molin, P.: Slab flattening and the rise of the Eastern Cordillera, Colombia. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 512, 100-110, 2019. (PDF)
- Becker, T. W., Lowry, A. R., Faccenna, C., Schmandt, B., Borsa, A., and Yu, C.: Western U.S. intermountain seismicity caused by changes in upper mantle flow. Nature, 524, 458-461, 2015. (PDF)
- Yarce, Y., Monsalve, G., Becker, T. W., Cardona, A., Poveda, E., Alvira, D., Ordoñez-Carmona, O.: Seismological observations in Northwestern South America: Evidence for two subduction segments, contrasting crustal thicknesses and upper mantle flow. Tectonophys., 637, 57-67, 2014. (PDF)
- Becker, T. W., Faccenna, C., Humphreys, E. D., Lowry, A. R., and Miller, M. S.: Static and dynamic support of western U.S. topography. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 402, 234-246, 2014. (PDF, dynamic topography models)
- Ghosh, A., Becker, T. W., and Humphreys, E. D.: Dynamics of the North American continent. Geophys. J. Int., 194, 651-669, 2013. (PDF)
- Becker, T.W., Behr, W.M., Brizzi, S., and Faccenna, C.: Subduction
dynamics and surface-deep mantle interactions. Keynote presentation
at the CSMDS meeting, Boulder CO, 2023.
Mediterrenean and Tethys
Regional studies focus on the margins of the Tethys, from the Mediterranean to Tibet.
- Castro-Perdomo, N., Jonsson, C., Klinger, Y., Masson, F., Becker, T. W., Johnson, J. Strain rates along the Alpine-Himalayan belt from a comprehensive GNSS velocity field. J. Geophys. Res.-Sol. Earth, doi:10.1029/2025JB031738, 2025. (PDF)
- Straume, E., Faccenna, C., Becker, T. W., Steinberger, B., Licht, A., Sembroni, A., Gvirtzman, Z., and Ballato, P.: Collision, mantle convection, and Tethyan closure in the Eastern Mediterranean. Nature Rev. Earth & Environ., 6, 299-317, 2025. (PDF)
- Sembroni, A., Faccenna, C., Becker, T. W., and Molin, P.: The uplift of the East Africa - Arabia swell, Earth-Sci. Rev., 257, 104901, 2024. (PDF)
- Straume, E. O., Steinberger, B., Becker, T. W., and Faccenna, C.: Impact of mantle convection and dynamic topography on the Cenozoic paleogeography of Central Eurasia and the West Siberian Seaway. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 630, 118615, 2024. (PDF)
- Lanari, R., Faccenna, C., Natali, C., Şengül Uluocak, E., Fellin, M. G., Becker, T.W., Göğüş, O., Youbi, N., Clementucci, R. and Conticelli, S.: The Atlas of Morocco: A Plume-Assisted Orogeny. G-Cubed, 24, doi:10.1029/2022GC010843, 2023. (PDF)
- Faccenna, C. and Becker, T. W.: Topographic expressions of mantle dynamics in the Mediterranean. Earth-Sci. Rev., 209, doi:10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103327, 2020. (PDF)
- Faccenna, C., Glisovic, P., Forte, A., Becker, T. W., Garzanti, E., Sembroni, A. and Gvirtzman, C.: Role of dynamic topography in sustaining the Nile River over 30 million years. Nat. Geosc., 12, 1012-1017, 2019. (PDF, UT News Release)
- Sternai, P., Sue, C., Husson, L., Serpelloni, E., Becker, T. W., Willett, S., Faccenna, C., Di Giulio, A., Spada, G., Jolivet, L., Valla, P., Petit, C., Nocquet, J.-M., Walpersdorf, A., and Castelltort, S.: Present-day uplift of the European Alps: evaluating mechanisms and models of their relative contributions Earth-Sci. Rev., 190, 589-604, 2019. (PDF)
- Sembroni, A., Faccenna, C., Becker, T. W., Molin, P., and Bekele, A.: Long-term, deep mantle support of the Ethiopia-Yemen plateau. Tectonics, 35, 469-488, doi:10.1002/2015TC004000, 2016. (PDF)
- Sternai, P., Avouac, J.-P., Jolivet, L., Faccenna, C., Gerya, T., Becker, T. W., and Menant, A.: Sub-crustal forcing on the tectonics and topography along the eastern Tibetan margin. J. Geodyn., doi:10.1016/j.jog.2016.02.009, 2016. (PDF)
- Sun, D., Miller, M. S., Holt, A. F., and Becker, T. W.: Hot upwelling conduit beneath the Atlas Mountains, Morocco. Geophys. Res. Lett., 41, 8037-8044, doi:10.1002/2014GL061884, 2014. (PDF, supp. mat.)
- Faccenna, C., Becker, T. W., Auer, L., Billi, A., Boschi, L., Brun, J.-P., Capitanio, F. A., Funiciello, F., Horvath, F., Jolivet, L., Piromallo, C., Royden, L., Rossetti, F., and Serpelloni, E.: Mantle dynamics in the Mediterranean. Rev. Geophys., 52, doi:10.1002/2013RG000444, 283--332, 2014. (PDF)
- Miller, M. S. and Becker, T. W.: Reactivated lithospheric-scale discontinuities localize dynamic uplift of the Moroccan Atlas Mountains. Geology, 42, 35-38, 2014. (PDF)
- Faccenna, C., Becker, T. W., Miller, M. S., Serpelloni, E., and
Willett, S. D.: Isostasy, dynamic topography, and the elevation of the
Apennines of Italy. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 407, 163-174,
2014. (PDF)
- TopoEurope presentation on topography in the Mediterranean mobile
belt with application to the Apeninnes and the Atlas (2014):
- TopoEurope presentation on topography in the Mediterranean mobile
belt with application to the Apeninnes and the Atlas (2014):
- Faccenna, C., Becker, T. W., Jolivet, L., and Keskin, M.: Mantle convection in the Middle East: Reconciling Afar upwelling, Arabia indentation and Aegean trench rollback. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 375, 254-269, 2013. (PDF)
- Faccenna, C. and Becker, T. W.: Shaping mobile belts by small-scale convection. Nature, 465, 602-605, 2010. (PDF)
- Boschi, L., Faccenna, C., and Becker, T. W.: Mantle structure and dynamic topography in the Mediterranean Basin. Geophys. Res. Lett., 37 (L20303), doi:10.1029/2010GL045001, 2010. (PDF)
Theory of convection induced topography
Explorations of the typical compensation mechanisms for different types of lithosphere in nature, as well as the expressions of plume and subduction systems in dynamic topography for free-slip and free surface conditions.
- Grima, A. G. and Becker, T. W.: The role of continental heterogeneity on the evolution of continental plate margin topography at subduction zones. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 642, 118856, 2024. (PDF)
- Sembroni, A., Kiraly, A., Faccenna, C., Funiciello, F., Becker, T. W., Globig, J., and Fernandez, M.: Impact of the lithosphere on dynamic topography: Insights from analogue modeling. Geophys. Res. Lett., 44, 2693-2702, doi:10.1002/2017GL072668, 2017. (PDF)
- Gvirtzman, Z., Faccenna, C., and Becker, T. W.: Isostasy, flexure, and dynamic topography. Tectonophys., 683, 255-171, 2016. (PDF)
- Kaus, B. J. P. and Becker, T. W.: A numerical study on the effects of surface boundary conditions and rheology on slab dynamics. Bolletino di Geofisica, 49(2), 177-182, 2008. (PDF)
- Kaus, B. J. P., Steedman, C., and Becker, T. W.: From passive continental margin to mountain belt: insights from analytical and numerical models and application to Taiwan. Phys. Earth Planet. Int., 171, 235-251, 2008. (PDF)
Small scale convection, volcanism, and intraplate tectonics
We evaluate the role of mantle convection in driving tectonic activity within plates and boundary zones for idealized models, and as applied to tectonically active continental regions such as the Mediterranean, the Middle East, the Horn of Africa, Tibet, and the western US.
- Sembroni, A., Faccenna, C., Becker, T. W., Molin, P., and Bekele, A.: Long-term, deep mantle support of the Ethiopia-Yemen plateau. Tectonics, 35, 469-488, doi:10.1002/2015TC004000, 2016. (PDF)
- Sun, D., Miller, M. S., Holt, A. F., and Becker, T. W.: Hot upwelling conduit beneath the Atlas Mountains, Morocco. Geophys. Res. Lett., 41, 8037-8044, doi:10.1002/2014GL061884, 2014. (PDF, supp. mat.)
- Miller, M. S. and Becker, T. W.: Reactivated lithospheric-scale discontinuities localize dynamic uplift of the Moroccan Atlas Mountains. Geology, 42, 35-38, 2014. (PDF)
- Faccenna, C., Becker, T. W., Jolivet, L., and Keskin, M.: Mantle convection in the Middle East: Reconciling Afar upwelling, Arabia indentation and Aegean trench rollback. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 375, 254-269, 2013. (PDF)
- Faccenna, C. and Becker, T. W.: Shaping mobile belts by
small-scale convection. Nature, 465, 602-605,
2010. (PDF)
- Faccenna, C., Becker, T. W., Lallemand, S., Lagabrielle, Y., Funiciello, F., and Piromallo, C.: Subduction-triggered magmatic pulses. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 209, 54-68, 2010.
- Faccenna, C., Rossetti, F., Becker, T. W., Danesi, S., and Morelli, A: Recent extension driven by mantle upwelling at craton edge beneath the Admirality Mountains (Ross Sea, East Antarctica). Tectonics, 27, TC4015, doi:10.1029/2007TC002197, 2008. (PDF)
Dynamics of the western United States
A multi-project effort to contribute to our understanding of Pacific-North America plate boundary processes on inter-seismic and geologic time-scales. We focus on forward models of stress and strain in the lithosphere based on geodetic, seismologic, and geodynamic information, and large-scale geodynamic models of mantle flow and subduction.
- Schulte-Pelkum, V., Becker, T. W., Behr, W. M., and Miller, M. S.: Tectonic inheritance during plate boundary evolution in southern California constrained from seismic anisotropy. Geochem., Geophys., Geosys., 22, doi:10.1029/2021GC010099, 2021. (PDF)
- Wang, W. and Becker, T. W.: Upper mantle seismic anisotropy as a constraint for mantle flow and continental dynamics of the North American Plate. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 514, 143-155, 2019. (PDF)
- Becker, T. W., Lowry, A. R., Faccenna, C., Schmandt, B., Borsa, A., and Yu, C. (2015): Western U.S. intermountain seismicity caused by changes in upper mantle flow. Nature, 524, 458-461. (PDF)
- Schmandt, B., Jacobsen, S. D., Becker, T. W., Liu, Z., and Dueker, K. G.: Dehydration melting at the top of the lower mantle. Science, 334, 1265-1268, 2014. (PDF)
- Becker, T. W., Faccenna, C., Humphreys, E. D., Lowry, A. R., and Miller, M. S.: Static and dynamic support of western U.S. topography. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 402, 234-246, 2014. (PDF, dynamic topography models)
- Ghosh, A., Becker, T. W., and Humphreys, E. D.: Dynamics of the North American continent. Geophys. J. Int., 194, 651-669, 2013. (PDF)
- Becker, T. W.: On recent seismic tomography for the western United States. Geochem., Geophys., Geosys., 13, Q01W10, doi:10.1029/2011GC003977, 2012. (PDF)
- Platt, J. P. and Becker, T. W.: Kinematics of rotating panels of E-W faults in the San Andreas system: what can we tell from geodesy? Geophys. J. Int., 194, 1295-1301, 2013. (PDF)
- Platt, J. P. and Becker, T. W.: Where is the real transform boundary in California? Geochem., Geophys., Geosys., 11(Q06013), doi:10.1029/2010GC003060, 2010. (PDF)
- Platt, J. P., Kaus, B. J. P. and Becker, T. W.: The mechanics of continental transforms: An alternative approach with applications to the San Andreas system and the tectonics of California. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 274, 380-391, 2008. (PDF)
- Fay, N. P. and T.W. Becker, and E. D. Humphreys: Southern California Modeling of Geodynamics in 3D (SMOG3D): Toward quantifying the state tectonic stress in the southern California crust, 2008 SCEC Annual Meeting Abstracts, 1-122, 2008.
- Becker, T. W., Schulte-Pelkum, V., Blackman, D. K., Kellogg, J. B., and O'Connell, R. J.: Mantle flow under the western United States from shear wave splitting, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 247, 235-251, 2006. (PDF)
- Becker, T. W., Hardebeck, J. L., and Anderson, G.: Constraints on fault slip rates of the southern California plate boundary from GPS velocity and stress inversions. Geophys. J. Int., 160, 634-650, 2005. (PDF).
- Becker, T. W. and Schmeling, H.: Earthquake recurrence time variations with and without fault zone interactions. Geophys. J. Int., 135, 165-176, 1998. (PDF)
Global planetary mantle dynamics
Generation of plate tectonics and mantle heterogeneity from convection
We use convection models to study which rheological laws, including damage memory, lead to plate-tectonic type of surface motions, and are able to match tomographically and kinematically inferred heterogeneity spectra self-consistently.
- Becker, T. W. and Fuchs, L.: Generation of evolving plate boundaries and toroidal flow from visco-plastic damage-rheology mantle convection and continents. G-Cubed, 24, e2023GC01117, doi:10.1029/2023GC011179, 2023. (PDF)
- Fuchs, L. and Becker, T. W.: On the role of rheological memory for convection-driven plate reorganizations. Geophys. Res. Lett., 49, e2022GL099574, 2022. (PDF)
- Becker, T. W., et al.: Global Scale Seismic Imaging and Dynamics of
the Earth's Mantle,
Talk
at College de France, Paris, 2021.

- Gerya, T.V., Bercovici, D., and Becker, T.W.: Dynamic slab segmentation due to brittle-ductile damage in the outer rise. Nature, 599, 245-250, 2021. (PDF)
- Fuchs, L. and Becker, T. W.: Deformation memory in the lithosphere: A comparison of damage-dependent weakening and grain-size sensitive rheologies J. Geophys. Res., 126, doi:10.1029/2020JB020335, 2020. (PDF)
- Fuchs, L. and Becker, T. W.: Role of strain-dependent weakening memory on the style of mantle convection and plate boundary stability. Geophys. J. Int., 218, 601-618, 2019. (PDF)
- Foley, B. and Becker, T. W.: Generation of plate-like behavior and
mantle heterogeneity from a spherical, visco-plastic convection
model. Geochem., Geophys., Geosys., 10, Q08001,
doi:10.1029/2009GC002378, 2009.
(PDF)
Also see our seismology inversions for vertical coherence of global structure and improved global models of shear wave structure:
- Porritt, R., Becker, T.W., Boschi, L., and Auer, L.: Multi-scale, radially anisotropic shear wave imaging of the mantle underneath the contiguous United States through joint inversion of USArray and global datasets. Geophys. J. Int., 2021. (PDF, SI, SAVANI-US model download)
- Auer, L., Boschi , L., Becker, T. W., Nissen-Meyer, T. and Giardini,
D.: Savani: a variable-resolution whole-mantle model of anisotropic
shear-velocity variations based on multiple datasets.
J. Geophys. Res., 119, 3006-3034, doi:10.1002/2013JB010773,
2014. (PDF,
model)
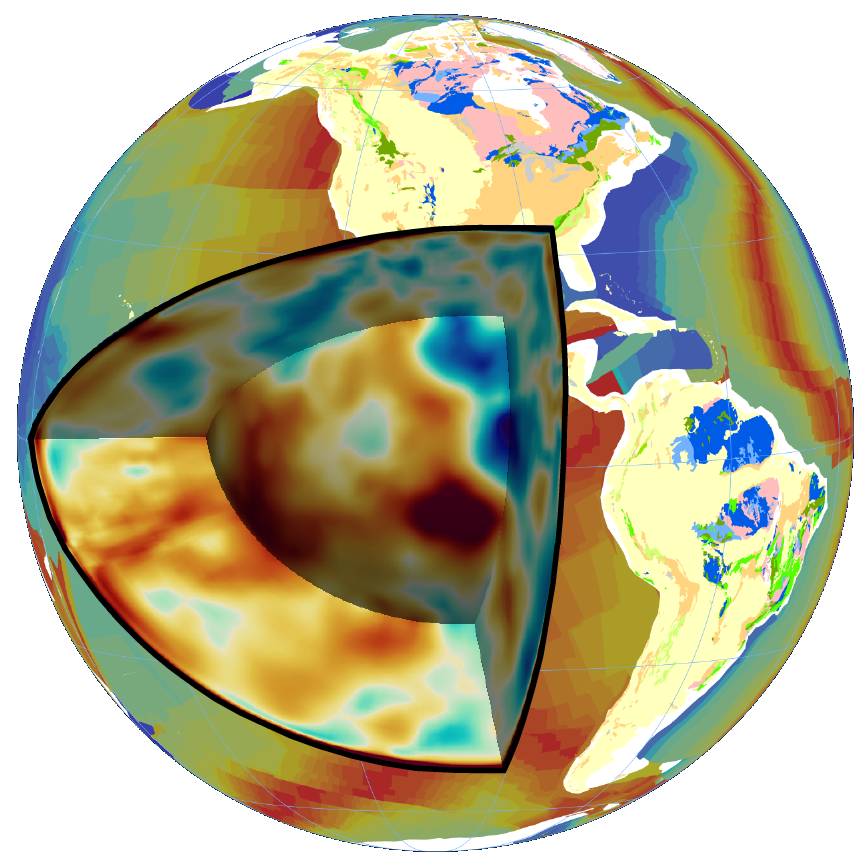
- Boschi, L. and Becker, T. W.: Vertical coherence in mantle heterogeneity from global seismic data. Geophys. Res. Lett., 38, (L20306), doi:10.1029/2011GL049281, 2011. (PDF)
Variability in plate tectonic heatflow over the Cenozoic and Earth's thermal evolution
We use reconstructions of seafloor age and plate geometry variations over the Cenozoic to infer the character of mantle heat transport and plate tectonic cyclicity, exploring subduction probabilities and the nature of the seafloor age vs. area relationship.
- Becker, T. W., Conrad, C. P., Buffett, B. and Müller, R. D.: Past and present seafloor age distributions and the temporal evolution of plate tectonic heat transport. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 278, 233-242, 2009. (PDF)
- Loyd, S. J., Becker, T. W., Conrad, C. P., Lithgow-Bertelloni, C., and Corsetti, F.A.: Time-variability in Cenozoic reconstructions of mantle heat flow: plate tectonic cycles and implications for Earth's thermal evolution Proceed. Nat. Acad. Sci., 104, 14266-14271, 2007. (PDF)
Mantle plume dynamics, detection, primordial reservoirs, and the origins of geochemical reservoirss
We analyze geodynamic and seismological models of the mantle and demonstrate that tomography images deep mantle plumes that connect to surface hotspots, if plume conduit distortion in the mantle wind is accounted for. We also analyze a range of geochemical and geophysical parameters to better understand the distribution of EM1, HIMU, and high 3/4He. In particular, the high 3/4He component appears associated with a primordial, deep mantle reservoir that is only entrained by the hottest plumes.
- Koppers, A., Becker, T.W., Jackson, M., Konrad, K., Müller, R.D., Romanowicz, B., Steinberger, B. and Whittaker, J.: Mantle plumes and their role in Earth processes. Nature Rev. Earth & Environ., 2, 382-401, 2021. (PDF)
- Jackson, M. G., Becker, T. W., and Steinberger, B.: Spatial characteristics of recycled and primordial reservoirs in the deep mantle. Geochem., Geophys., Geosys., 22, doi:10.1029/2020GC009525, 2021. (PDF)
- Jackson, M. G., Blichert-Toft, J., Halldórsson, S. A., Mundl-Petermeier, A., Bizimis, M., Kurz, M. D., Price, A. A., Harðardóttir, S., Willhite, L. N., Breddam, K., Becker T. W., and Fischer, R. A.: Ancient helium and tungsten isotopic signatures preserved in mantle domains least modified by crustal recycling. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci., 117, 30,993-31,001, 2020. (PDF)
- Jackson, M.G., Becker, T. W., and Konter, J. G.: Geochemistry and distribution of recycled domains in the mantle inferred from Nd and Pb isotopes in oceanic hotspots: implications for storage in the large low shear wave velocity provinces (LLSVPs) G-Cubed, 19, 3496-3519, doi:10.1029/2018GC007552, 2018. (PDF)
- Jackson, M. G., Becker, T. W., and Konter, J. G.: Evidence for a deep mantle source for EM and HIMU domains from integrated geochemical and geophysical constraints. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 484, 154-167, 2018. (PDF)
- Jackson, M. G., Konter, J. G., and Becker, T. W.: Primordial helium entrained by the hottest mantle plumes. Nature, 542, 340-343, 2017. (PDF)
- Konter, J. G. and Becker, T. W.: Shallow lithospheric contribution to mantle plumes revealed by integrating seismic and geochemical data. Geochem., Geophys., Geosys., 13, Q02004, doi:10.1029/2011GC003923, 2012. (PDF)
- Boschi, L., Becker, T. W., and Steinberger, B.: On the statistical significance of correlations between synthetic mantle plumes and tomographic models. Physics Earth Planet. Int., 260, 230-238, 2008. (PDF)
- Boschi, L., T. W. Becker, and B. Steinberger, Mantle plumes: Dynamic models and seismic images, Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst., 8, Q10006, doi:10.1029/2007GC001733, 2007. (PDF)
Plume talk-back terminating subduction
We use convection models with damage rheologies to show that slabs can not only trigger plume upwellings at the CMB, but plumes arising along slabs may shut off subduction at the surface. This bottom-up interaction may have been relevant particularly for the early Earth.
- Heilman, E. and Becker, T. W.: Plume-driven subduction termination in 3-D mantle convection models. G-Cubed, 25, doi:10.1029/2024GC011523, 2024. (PDF)
- Heilman, E. and Becker, T. W.: Plume-slab interactions can shut off subduction. Geophys. Res. Lett., 49, e2022GL099286, 2022. (PDF)
- Gerya, T. V., Bercovici, D., and Becker, T. W.: Dynamic slab segmentation due to brittle-ductile damage in the outer rise. Nature, 599, 245-250, 2021. (PDF)
20 years of linking seismic topography and mantle convection
Convection in icy satellites
We explore convection in thin shells as applied to the icy satellites of solar system moons such as Enceladus and Europa.
- Weller, M. B., Fuchs, L., Becker, T. W., and Soderlund, K. M.: Convection in thin shells of icy satellites: Effects of latitudinal surface temperature variations. J. Geophys. Res. - Planets, 124, 2029-2053, 2019. (PDF)
Plate velocities, mantle flow, and lithospheric deformation
We have several ongoing collaborative efforts to refine our understanding of global and regional mantle circulation, subduction, what tractions might be expected to be transmitted to the lithosphere, why the plates move the way they do, and which geological processes might be associated with a deep mantle origin.Mantle convection, conveyor belts, and orogeny
- Straume, E. O., Steinberger, B., Becker, T. W., and Faccenna, C.: Impact of mantle convection and dynamic topography on the Cenozoic paleogeography of Central Eurasia and the West Siberian Seaway. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 630, 118615, 2024. (PDF)
- Jyotirmoy, P., Conrad, C. P., Becker, T. W., and Ghosh, A.: Convective self-compression of cratons and the stabilization of old lithosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett., 50, doi:10.1029/2022GL101842, 2023. ( PDF)
- Faccenna, F., Becker, T. W., Holt, A. F., and Brun, J. P.: Mountain building, mantle convection, and supercontinents: Holmes (1931) revisited. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 564, Frontiers, 116905, 2021. (PDF)
- Jolivet, L., Faccenna, C., Becker, T. W., Tesauro, M., Sernai, P., and Bouihol, P.: Mantle flow and deforming continents: From India-Asia convergence to Pacific subduction. Tectonics, doi:10.1029/2018TC005036, 2018. (PDF)
- Faccenna, C., Oncken, O., Holt, A. F., and Becker, T. W.: Initiation of the Andean orogeny by lower mantle subduction. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 463, 189-201, 2017. (PDF)
- Yamato, P., Husson, L., Becker, T. W., and Pedoja, K.: Passive margins getting squeezed in the mantle convection vice. Tectonics, 32, 1599-1570, doi: 10.1002/2013TC003375, 2013. (PDF)
- Faccenna, C., Becker, T. W., Conrad, C. P., and Husson, L.: Mountain building and mantle dynamics. Tectonics, 32, 80-93, doi:10.1029/2012TC003176, 2013. (PDF)
- Becker, T. W. and Faccenna, C.: Mantle conveyor beneath the Tethyan collisional belt. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 310, 453-461, 2011. (PDF, suppl. mat.).
Global mantle convection and generation of plate tectonics
- Becker, T. W. and Fuchs, L.: Generation of evolving plate boundaries and toroidal flow from visco-plastic damage-rheology mantle convection and continents. G-Cubed, 24, e2023GC011179, doi:10.1029/2023GC011179, 2023. (PDF)
- Clennett, E. J., Holt, A. F, Tetley, M. G., Becker, T. W., and Faccenna, C.: Assessing plate reconstruction model using plate driving force consistency tests. Sci. Rep., doi:10.1038/srep2300487, 2023. (PDF)
- Fuchs, L. and Becker, T. W.: On the role of rheological memory for convection-driven plate reorganizations. Geophys. Res. Lett., 49, e2022GL099574, 2022. (PDF)
- Fuchs, L. and Becker, T. W.: Role of strain-dependent weakening memory on the style of mantle convection and plate boundary stability. Geophys. J. Int., 218, 601-618, 2019. (PDF)
- Becker, T. W.: Superweak asthenosphere in light of upper-mantle seismic anisotropy, Geochem., Geophys., Geosys., 18, 1986-2003, doi:10.1002/2017GC006886, 2017. (PDF)
- Becker, T. W., Schaeffer, A. J., Lebedev, S., and Conrad, C. P.: Toward a generalized plate motion reference frame. Geophys. Res. Lett., 42, doi:10.1002/2015GL063695, 3188-3196, 2015. (PDF, supp. mat., model)
- Gérault, M. and Becker, T. W. and Kaus, B. J. K. and Faccenna, L. and Moresi, L. N. and Husson, L.: The role of slabs and oceanic plate geometry for the net rotation of the lithosphere, trench motions, and slab return flow. Geochem., Geophys., Geosys., 13, Q04001, doi:10.1029/2011GC003934, 2012. (PDF)
- Becker, T. W. and Kawakatsu, H.: On the role of anisotropic viscosity for plate-scale flow. Geophys. Res. Lett., 38, L17307, doi:10.1029/2011GL048584, 2011. (PDF)
- Becker, T. W.: Fine-Scale Modeling of Global Plate Tectonics. Science, 329, 1020-1021, 2010. (PDF)
- Ghosh, A., Becker, T. W., and Zhong, S.: Effects of lateral viscosity variations on the geoid. Geophys. Res. Lett., 37, L01301, doi:10.1029/2009GL040426, 2010. (PDF).
- Bull, A. L., McNamara, A. K., Becker, T. W., and Ritsema, J.: Global scale models of the mantle flow field predicted by synthetic tomography models. Phys. Earth Planet. Int., 182, 129-138, 2010. (PDF)
- Becker, T. W.: On the effect of temperature and strain-rate dependent viscosity on global mantle flow, net rotation, and plate-driving forces. Geophys. J. Int., 167, 943-957, 2006. (PDF)
- Becker, T. W. and O'Connell, R. J.: Predicting plate motions with mantle circulation models, Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2(12), doi:10.1029/2001GC000171, 2001. (PDF)
- Becker, T. W. and O'Connell, R. J.: Lithospheric stresses caused by mantle convection: the role of plate rheology (abstract) EOS Trans. AGU, 82, T12C-0921, 2001. (PDF)
Regional dynamics
- Holt, A. F., Royden, L. H., and Becker, T. W.: The dynamics of double slab subduction. Geophys. J. Int., 209, 250-265, 2017. (PDF, supp. mov.)
- Holt, A. F. and Becker, T. W.: The effect of a power-law mantle viscosity on trench retreat rate. Geophys. J. Int., 208, 491-507, 2017. (PDF)
- Sternai, P., Avouac, J.-P., Jolivet, L., Faccenna, C., Gerya, T., Becker, T. W., and Menant, A.: Sub-crustal forcing on the tectonics and topography along the eastern Tibetan margin. J. Geodyn., doi:10.1016/j.jog.2016.02.009, 2016. (PDF)
- Schmandt, B., Jacobsen, S. D., Becker, T. W., Liu, Z., and Dueker, K. G.: Dehydration melting at the top of the lower mantle. Science, 334, 1265-1268, 2014. (PDF)
- Faccenna, C., Becker, T. W., Jolivet, L., and Keskin, M.: Mantle convection in the Middle East: Reconciling Afar upwelling, Arabia indentation and Aegean trench rollback. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 375, 254-269, 2013. (PDF)
- Faccenna, C., Becker, T. W., Lallemand, S., and Steinberger, B.: On the role of slab pull in the Cenozoic motion of the Pacific. Geophys. Res. Lett., 39, L03305, doi:10.1029/2011GL050155, 2012. (PDF)
- Faccenna, C. and Becker, T. W.: Shaping mobile belts by small-scale convection. Nature, 465, 602-605, 2010. (PDF)
- Kaus, B, Liu, Y., Becker, T. W., Yuen, D., and Shi, Y.: Lithospheric stress-states predicted from long-term tectonic models: influence of rheology and possible application to Taiwan. J. Asian Earth Sci., 36, 119-134, 2009. (PDF)
Thermal constraints on the survival of primitive blobs in the lower mantle
We examine mantle blobs, a mantle convection model that could reconcile geochemical data with geophysical evidence for whole mantle convection. Our analytical model shows that stiff blobs could serve as a geochemical reservoir over geologically long timescales even if they were to heat up by means of enrichment in heat producing elements.
- Becker, T. W., Kellogg, J. B., and O'Connell, R. J.: Thermal constraints on the survival of primitive blobs in the lower mantle. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 171, 351-365, 1999. (PDF)
A global comparison of seismologic and geodynamic mantle models
We present comparisons between global seismological and geodynamic models of the Earth's mantle to help in the move from mapping to hypotheses testing. Our results are compatible with whole mantle convection with reorganization of flow at 660-km due to the viscosity jump and provide insights on time-dependent plate tectonics and the state of thermo-chemical convection in the mantle.
- Steinberger, B., Torsvik, T. H., and Becker, T. W.: Subduction to the lower mantle - a comparison between geodynamic and tomographic models. Solid Earth, 3, 415-432, 2012. (PDF)
- Becker, T. W. and Boschi, L.: A comparison of tomographic and geodynamic mantle models, Geochem., Geophys., Geosys., 3(1), 1003, doi:10.1029/2001GC000168, 2002. (PDF)
Additional online material for Becker and Boschi (2002) can be found on the correlations between tomographic models page. All models from that paper, and a few newer ones, can be used directly as input for the hc global mantle flow program, as provided in the Solid Earth Research and Teaching Environment (SEATREE).
- Milner, K., Becker, T. W., Boschi, L., Sain, J., Schorlemmer, D. and H. Waterhouse: The Solid Earth Research and Teaching Environment: a new software framework to share research tools in the classroom and across disciplines. Eos Trans. AGU, 90, 12, 2009. (PDF).
- Waterhouse, H. D., K. Milner, T. W. Becker, J. Sain, and D. Schorlemmer: A Solid Earth Research and Teaching Environment, Opportunities and Challenges in Computational Geophysics workshop, Caltech, 2009. (PDF).
Global semi-analytical flow code benchmark
Supported by CIG's Mantle Convection working group, I am coordinating a benchmark and recoding effort to establish a shared, modular and flexible implementation of a Hager & O'Connell (1981) type program for solving for velocities in the viscous mantle. Download instructions for the code are found here (under: hc). You can download the work plan with summary of results as PDF here; please send me an email if you would like to participate in this effort.
As a product of this effort, a simple, modular, C-language implementation, hc, is available. HC is a module within the Solid Earth Research and Teaching (SEATREE) environment.
Seismic anisotropy and upper mantle dynamics
Seismic anisotropy from global mantle flow LPO model
A comprehensive reference frame for present-day plate motions
We show that a spreading-aligned absolute plate motion reference frame can be constructed and fits a number of observations, including azimuthal anisotropy and hotspot motions, well. This has implications for transform fault weakness, passive spreading, and trench motions statistics.- Schaeffer, A., Lebedev, S., and Becker, T. W.: Azimuthal seismic anisotropy in the Earth's upper mantle and the thickness of tectonic plates. Geophys. J. Int., 207, 901-933, 2016. (PDF, supp. mat.)
- Becker, T. W., Schaeffer, A. J., Lebedev, S., and Conrad, C. P.: Toward a generalized plate motion reference frame. Geophys. Res. Lett., 42, doi:10.1002/2015GL063695, 3188-3196, 2015. (PDF, supp. mat.)
- download plate velocities in new reference frame
Regional anisotropy and lithosphere-asthenosphere interactions
We study regional shear wave splitting, receiver function, and surface wave based lithospheric and mantle anisotropy for the North and South American Cordillera, the the Mediterranean and Alaska, and interpret them in terms of upper mantle, small-scale convection, slab-keel interactions, and lithospheric deformation.
- Hua, J., Schulte-Pelkum, V., Becker, T. W., He, B., and Zhu, H.: Waveform effects on shear wave splitting near fault zones. J. Geophys. Res.-Sol. Earth, doi:10.1029/2025JB031656, 2025. (PDF)
- Liu, C., Becker, T. W., Wu, M., Han, S., and Ritzwoller, M. H.: Seismic azimuthal anisotropy within the Juan de Fuca - Gorda plate system. Geophys. Res. Lett., doi:10.1029/2024GL111835, 2024. (PDF)
- Schulte-Pelkum, V., Becker, T. W., Behr, W. M., and Miller, M. S.: Tectonic inheritance during plate boundary evolution in southern California constrained from seismic anisotropy. Geochem., Geophys., Geosys., 22, doi:10.1029/2021GC010099, 2021. (PDF)
- Schulte-Pelkum, V., Cain, J. S, Jones II, J. V., and Becker, T. W: Imaging the tectonic grain of the Northern Cordillera orogen using Transportable Array receiver functions. Seismol. Res. Lett., 91, 3086-3105, 2020. (PDF, SI)
- Wang, W. and Becker, T. W.: Upper mantle seismic anisotropy as a constraint for mantle flow and continental dynamics of the North American Plate. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 514, 143-155, 2019. (PDF)
- Jolivet, L., Faccenna, C., Becker, T. W., Tesauro, M., Sternai, P., and Bouihol, P.: Mantle flow and deforming continents: From India-Asia convergence to Pacific subduction. Tectonics, 37, 2887-2914, doi:10.1029/2018TC005036, 2018. (PDF)
- Porritt, R. W., Becker, T. W., and Monsalve, G.: Seismic anisotropy and slab dynamics from SKS splitting recorded in Colombia. Geophys. Res. Lett., 41, doi:10.1002/2014GL061958, 2014. (PDF)
- Faccenna, C., Becker, T. W., Auer, L., Billi, A., Boschi, L., Brun, J.-P., Capitanio, F. A., Funiciello, F., Horvath, F., Jolivet, L., Piromallo, C., Royden, L., Rossetti, F., and Serpelloni, E.: Mantle dynamics in the Mediterranean. Rev. Geophys., 52, doi:10.1002/2013RG000444, 2014. (PDF)
- Miller, M. S. and Becker, T. W.: Reactivated lithospheric-scale
discontinuities localize dynamic uplift of the Moroccan Atlas
Mountains. Geology, 42, 35-38, 2014.
(PDF)
- Miller, M. S. and Becker, T. W.: Reactivated lithospheric-scale discontinuities localize dynamic uplift of the Moroccan Atlas Mountains: Comment - Reply. Geology, 42, 338, 2014. (PDF)
- Nature Geoscience highlight by Whitchuch
- USC News release
- Miller, M. S., Allam, A. A., Becker, T. W., Di Leo, J., and Wookey, J.: Constraints on the geodynamic evolution of the westernmost Mediterranean and northwestern Africa from shear wave splitting analysis. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 375, 234-243, 2013. (PDF)
- Alpert, L. A., Miller, M. S., Becker, T. W., and Allam, A. A.: Structure beneath the Alboran from geodynamic flow models and seismic anisotropy. J. Geophys. Res., 118, 1-13, doi:10.1002/jgrb.50309, 2013. (PDF)
- Faccenna, C., Becker, T. W., Jolivet, L., and Keskin, M.: Mantle convection in the Middle East: Reconciling Afar upwelling, Arabia indentation and Aegean trench rollback. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 375, 254-269, 2013. (PDF, velocity grids)
- Miller, M. S. and Becker, T. W.: Mantle flow deflected by interactions between subducted slabs and cratonic keels. Nature Geosc., 5, 726-730, 2012. (PDF)
- Becker, T. W., Schulte-Pelkum, V., Blackman, D. K., Kellogg, J. B., and O'Connell, R. J.: Mantle flow under the western United States from shear wave splitting, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 247, 235-251, 2006. (PDF)
Review articles and chapters on seismic anisotropy
- Becker, T. W. and Lebedev, S.: Dynamics of the upper mantle in light of seismic anisotropy. In Mantle Convection and Surface Expressions, Cottaar, S.. et al., eds., AGU, Washington DC, doi:10.1002/9781119528609.ch10, 2020. (PDF)
- Long, M. D. and Becker, T. W.: Mantle dynamics and seismic anisotropy. Earth Planet Sci. Lett., 297, Frontiers, 341-354, 2010. (PDF).
- Becker, T. W.: Seismic anisotropy. In Encyclopedia of Solid Earth Geophysics, Gupta, H. (Ed.), doi:10.1007/978-90-481-8702-7_51, p. 1070-1081, Springer, 2010. (PDF, HTML)
- See also:
Radial anisotropy as a constraint for regional tectonics, mantle rheology, and volatile content
We explore radial anisotropy by means of improved global and regional imaging and forward models based on stochastic and mantle flow computations. The geoynamic models are able to match both global radial anisotropy averages and most of the anomaly patterns. The mismatch between seismology and geodynamic reference, residual anisotropy, yields information on the frozen-in structure of the oceanic and continental lithosphere and the volatile and melt content and viscosity of the asthenosphere.
- Seismic anisotropy from global mantle flow model download
- Hua, J., Grand, S. P., Becker, T. W., Janiszewski, H., Liu, C., Trugman, D., and Zhu, H: Seismic full-waveform tomography of active cratonic thinning beneath North America consistent with slab-induced dripping. Nature Geosc., doi:10.1038/s41561-025-01671-x, 2025. (PDF)
- Hua, J., Fischer, K., Becker, T.W., Gazel, E. and Hirth, G.: Asthenospheric low-velocity zone consistent with globally prevalent partial melting. Nature Geosc., 16, 175-181, 2023. (PDF)
- Porritt, R., Becker, T.W., Boschi, L., and Auer, L.: Multi-scale, radially anisotropic shear wave imaging of the mantle underneath the contiguous United States through joint inversion of USArray and global datasets. Geophys. J. Int., 265, 1730--1746, 2021. (PDF, SI, SAVANI-US model download)
- Auer, L., Becker, T. W., Boschi, L., and Schmerr, N.: Thermal structure, radial anisotropy, and dynamics of oceanic boundary layers. Geophys. Res. Lett., 42, 9740-9749, doi:10.1002/2015GL06624, 2015. (PDF)
- Auer, L., Boschi , L., Becker, T. W., Nissen-Meyer, T. and Giardini, D.: Savani: a variable-resolution whole-mantle model of anisotropic shear-velocity variations based on multiple datasets. J. Geophys. Res., 119, 3006-3034, doi:10.1002/2013JB010773, 2014. (PDF, model)
- Schaefer, J. F., Boschi, L., Becker, T. W. and Kissling, E.: Radial anisotropy in the European mantle: Tomographic studies explored in terms of mantle flow. Geophys. Res. Lett., 38 (L23304), doi:10.1029/2011GL049687, 2011. (PDF).
- Becker, T. W., Kustowski, B. and Ekström, G.: Radial seismic anisotropy as a constraint for upper mantle rheology. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 267, 213-237, 2008. (PDF, model)
Anisotropy provides a speed limit for net rotations
We show that anisotropy constrains net rotations of the lithosphere to be smaller than in some hotspot reference frame models, and that spreading-aligned plate motion reference frames are consistent with azimuthal anisotropy.
- Becker, T. W., Schaeffer, A. J., Lebedev, S., and Conrad, C. P.: Toward a generalized plate motion reference frame. Geophys. Res. Lett., 42, doi:10.1002/2015GL063695, 3188-3196, 2015. (PDF, supp. mat., model)
- Becker, T. W.: Azimuthal seismic anisotropy constrains net rotation of the lithosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett., 35, L05303, doi:10.1029/2007GL032928, 2008. (Correction: 2008GL033946, PDF)
- Becker, T. W., Ekström, G., Boschi, L., and Woodhouse, J.: Length scales, patterns, and origin of azimuthal seismic anisotropy in the upper mantle as mapped by Rayleigh waves. Geophysical J. Int., 171 451-462, 2007. (PDF)
Length scales and origin of upper mantle anisotropy
We analyze the lateral variations in anisotropic length scales as inferred from SKS splitting and azimuthal anisotropy tomography, and CPO field studies.
- seismic anisotropy from global mantle flow model download
- JSG Geodynamics SKS splitting compilation, previous version used in Becker et al. (2012).
- Wolf, J., Becker, T.W., Garnero, E., Liu, K. H. and West, J.D. (2025): Comprehensive global dataset of uniformly processed shear-wave splitting measurements. Geophys. J. Int., 241, 863–875. (PDF)
- Bernard, R., Behr, W. M., Becker, T. W., and Young, D.: Relationships between olivine CPO and deformation parameters in naturally deformed rocks and implications for mantle seismic anisotropy. Geochem., Geophys., Geosys., 20, 1-27, doi:10.1029/2019GC008289, 2019. (PDF)
- Becker, T. W., Lebedev, S., and Long, M. D.: On the relationship between azimuthal anisotropy from shear wave splitting and surface wave tomography. J. Geophys. Res., 117, B01306, doi:10.1029/2011JB008705, 2012. (PDF)
- Becker, T. W., Browaeys, J. T., and Jordan, T. H.: Stochastic Analysis of Shear Wave Splitting Length Scales. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 259, 526-540, 2007. (PDF)
- Becker, T. W., Ekström, G., Boschi, L., and Woodhouse, J.: Length scales, patterns, and origin of azimuthal seismic anisotropy in the upper mantle as mapped by Rayleigh waves. Geophysical J. Int., 171 451-462, 2007. (PDF)
Mantle flow, crytallographic (or lattice) preferred orientation (CPO/LPO) fabrics, and viscous anisotropy
We study upper mantle fabrics from field samples and theoretical texturing models and mantle convection models. We also explore the role of mechanical anisotropy for boundary layer flow. Previously NSF-CSEDI funded.
- seismic anisotropy from global mantle flow model download
- Gupta, A., Tape, C., Brown, J. M., and Becker, T. W.: Navigating the space of seismic anisotropy for crystal and whole-Earth scales. Geophys. J. Int., 242, 1-18, 2025. (PDF)
- Liu, D., Puel, S., Becker, T. W., and Moresi, L. N.: Analytical and numerical models of viscous anisotropy: A toolset to constrain the role of mechanical anisotropy for regional tectonics and fault loading. Geophys. J. Int., 239, 950-963, 2024.
- Bernard, R., Behr, W. M., Becker, T. W., and Young, D.: Relationships between olivine CPO and deformation parameters in naturally deformed rocks and implications for mantle seismic anisotropy. Geochem., Geophys., Geosys., doi:10.1029/2019GC008289, 2019. (PDF)
- Wang, W. and Becker, T. W.: Upper mantle seismic anisotropy as a constraint for mantle flow and continental dynamics of the North American Plate. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 514, 143-155, 2019. (PDF)
- Becker, T. W.: Superweak asthenosphere in light of upper-mantle seismic anisotropy, Geochem., Geophys., Geosys., 18, 1986-2003, doi:10.1002/2017GC006886, 2017. (PDF)
- Schaeffer, A., Lebedev, S., and Becker, T. W.: Azimuthal seismic anisotropy in the Earth's upper mantle and the thickness of tectonic plates. Geophys. J. Int., 207, 901-933, 2016. (PDF, supp. mat.)
- Auer, L., Becker, T. W., Boschi, L., and Schmerr, N.: Thermal structure, radial anisotropy, and dynamics of oceanic boundary layers. Geophys. Res. Lett., 42, 9740-9749, doi:10.1002/2015GL066246, 2015. (PDF)
- Becker, T. W., Conrad, C. P., Schaeffer, A. J., and Lebedev, S.: Origin of azimuthal seismic anisotropy in oceanic plates and mantle. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 401, 246-250, 2014. (PDF, model)
- Becker, T. W. and Kawakatsu, H.: On the role of anisotropic viscosity for plate-scale flow. Geophys. Res. Lett., 38, L17307, doi:10.1029/2011GL048584, 2011. (PDF)
- Castelnau, O., Blackman, D. K. and Becker, T. W.: Numerical simulations of texture development and associated rheological anisotropy in regions of complex mantle flow. Geophys. Res. Lett, 36, L12304, doi:10.1029/2009GL038027, 2009. (PDF)
- Becker, T. W., Ekström, G., Boschi, L., and Woodhouse, J.: Length scales, patterns, and origin of azimuthal seismic anisotropy in the upper mantle as mapped by Rayleigh waves. Geophysical J. Int., 171 451-462, 2007. (PDF)
- Becker, T. W., Chevrot, S., Schulte-Pelkum, V., and Blackman, D. K.: Statistical properties of seismic anisotropy predicted by upper mantle geodynamic models. J. Geophys. Res., 111, B08309, doi:10.1029/2005JB004095, 2006. (PDF).
- Becker, T. W., Kellogg, J. B., Ekström, G., and O'Connell, R. J.: Comparison of azimuthal seismic anisotropy from surface waves and finite-strain from global mantle-circulation models, Geophys. J. Int., 155, 696-714, 2003. (PDF)
[news] [teaching] [team] [publications] [CV] [downloads] [contact]
[geodynamics] [seismology] [fieldwork] [downloads] [lab]
[subduction] [dynamic topography] [global dynamics] [western US] [anisotropy]